Contents
目录
Foreword
前言
Introduction
引言
0.1 General
0.1 总则
0.2 Quality management principles
0.2 质量管理原则
0.3 Process approach
0.3 过程方法
0.3.1 General
0.3.1 总则
0.3.2 Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle
0.3.2 策划-实施-检查-处置(PDCA)循环
0.4 Relationship with other management system standards
0.4 与其他管理体系标准的关系
1 Scope
1 范围
2 Normative references
2 规范性引用文件
3 Terms and definitions
3 术语和定义
4 Context of the organization
4 组织环境
4.1 Understanding the organization and its context
4.1 理解组织及其环境
4.2 Understanding the needs and expectations of interested parties
4.2 理解相关方的需求和期望
4.3 Determining the scope of the quality management system
4.3 确定质量管理体系的范围
4.4 Quality management system
4.4 质量管理体系
5 Leadership
5 领导作用
5.1 Leadership and commitment
5.1 领导作用和承诺
5.1.1 General
5.1.1 总则
5.1.2 Customer focus
5.1.2 以顾客为关注焦点
5.2 Quality policy
5.2 质量方针
5.3 Roles, responsibilities and authorities
5.3 组织的角色、职责和权限
6 Planning
6 策划
6.1 Actions to address risks and opportunities
6.1 应对风险和机遇的措施
6.1.1 Determining risks and opportunities
6.1.1 确定风险和机遇
6.1.2 Actions to address risks
6.1.2 应对风险的措施
6.1.3 Actions to address opportunities
6.1.3 应对机遇的措施
6.2 Quality objectives and planning to achieve them
6.2 质量目标及其实现的策划
6.3 Planning of changes
6.3 变更的策划
7 Support
7 支持
7.1 Resources
7.1 资源
7.1.1 General
7.1.1 总则
7.1.2 People
7.1.2 人员
7.1.3 Infrastructure
7.1.3 基础设施
7.1.4 Environment for the operation of processes
7.1.4 过程运行的环境
7.1.5 Monitoring and measuring resources
7.1.5 监视和测量资源
7.1.6 Organizational knowledge
7.1.6 组织知识
7.2 Competence
7.2 能力
7.3 Awareness
7.3 意识
7.4 Communication
7.4 沟通
7.5 Documented information
7.5 形成文件的信息
7.5.1 General
7.5.1 总则
7.5.2 Creating and updating documented information
7.5.2 创建和更新形成文件的信息
7.5.3 Control of documented information
7.5.3 对形成文件的信息的控制
8 Operation
8 运行
8.1 Operational planning and control
8.1 运行策划和控制
8.2 Requirements for products and services
8.2 产品和服务的要求
8.2.1 Customer communication
8.2.1 顾客沟通
8.2.2 Determining the requirements for products and services
8.2.2 确定产品和服务的要求
8.2.3 Review of the requirements for products and services
8.2.3 评审产品和服务的要求
8.2.4 Changes to requirements for products and services
8.2.4 产品和服务要求的变更
8.3 Design and development of products and services
8.3 产品和服务的设计和开发
8.3.1 General
8.3.1 总则
8.3.2 Design and development planning
8.3.2 设计和开发策划
8.3.3 Design and development inputs
8.3.3 设计和开发输入
8.3.4 Design and development controls
8.3.4 设计和开发控制
8.3.5 Design and development outputs
8.3.5 设计和开发输出
8.3.6 Design and development changes
8.3.6 设计和开发变更
8.4 Control of externally provided processes, products and services
8.4 外部提供的过程、产品和服务的控制
8.4.1 General
8.4.1 总则
8.4.2 Type and extent of control
8.4.2 控制的类型和程度
8.4.3 Information for external providers
8.4.3 给外部提供方的信息
8.5 Production and service provision
8.5 生产和服务提供
8.5.1 Control of production and service provision
8.5.1 生产和服务提供的控制
8.5.2 Identification and traceability
8.5.2 标识和可追溯性
8.5.3 Property belonging to customers or external providers
8.5.3 顾客或外部提供方的财产
8.5.4 Preservation
8.5.4 防护
8.5.5 Post-delivery activities
8.5.5 交付后活动
8.5.6 Control of changes
8.5.6 变更控制
8.6 Release of products and services
8.6 产品和服务的放行
8.7 Control of nonconforming outputs
8.7 不合格输出的控制
9 Performance evaluation
9 绩效评价
9.1 Monitoring, measurement, analysis and evaluation
9.1 监视、测量、分析和评价
9.1.1 General
9.1.1 总则
9.1.2 Customer satisfaction
9.1.2 顾客满意
9.1.3 Analysis and evaluation
9.1.3 分析和评价
9.2 Internal audit
9.2 内部审核
9.2.1 General
9.2.1 总则
9.2.2 Internal audit programme
9.2.2 内部审核方案
9.3 Management review
9.3 管理评审
9.3.1 General
9.3.1 总则
9.3.2 Management review inputs
9.3.2 管理评审输入
9.3.3 Management review results
9.3.3 管理评审结果
10 Improvement
10 改进
10.1 Continual improvement
10.1 持续改进
10.2 Nonconformity and corrective action
10.2 不合格和纠正措施
Annex A (informative) Clarification of structure, terminology and clauses
附录A (资料性附录)结构、术语和条款的说明
Bibliography
参考文献
Foreword
前言
ISO (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide federation of national standards bodies (ISO member bodies). The work of preparing International Standards is normally carried out through ISO technical committees. Each member body interested in a subject for which a technical committee has been established has the right to be represented on that committee. International organizations, governmental and non-governmental, in liaison with ISO, also take part in the work. ISO collaborates closely with the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) on all matters of electrotechnical standardization.
ISO (国际标准化组织)是各国国家标准机构(ISO 成员机构)的世界性联合会。国际标准的制定工作通常由ISO 技术委员会完成。每个对已成立技术委员会的某一主题感兴趣的成员机构,都有权派代表参加该委员会。与ISO 保持联系的政府性和非政府性国际组织也参与此项工作。在电工技术标准化的所有事务上,ISO与国际电工委员会(IEC) 紧密合作。
The procedures used to develop this document and those intended for its further maintenance are described in the ISO/IEC Directives, Part 1. In particular, the different approval criteria needed for the different types of ISO documents should be noted. This document was drafted in accordance with the editorial rules of the ISO/IEC Directives, Part 2 (seewww.iso.org/directives).
用于制定本文件以及对其进行后续维护的程序,在ISO/IEC 指南第1部分中有描述。特别应注意,不同类型的 ISO 文件需要不同的批准准则。本文件是根据 ISO/IEC 指南第2部分的编辑规则起草的 (见 www.iso.org/directives)。
ISO draws attention to the possibility that the implementation of this document may involve the use of (a) patent(s). ISO takes no position concerning the evidence, validity or applicability of any claimed patent rights in respect thereof. As of the date of publication of this document, ISO had not received notice of (a) patent(s) which may be required to implement this document. However, implementers are cautioned that this may not represent the latest information, which may be obtained from the patent database available atwww.iso.org/patents. ISO shall not be held responsible for identifying any or all such patent rights.
ISO 提请注意,本文件的实施可能涉及一项或多项专利的使用。ISO对任何声称的专利权的证据、有效性或适用性不持立场。截至本文件发布之日,ISO尚未收到任何实施本文件可能需要的专利通知。然而,提醒实施者注意,这可能不是最新信息,最新信息可从 www.iso.org/patents 的专利数据库中获取。ISO 不承担识别任何或所有此类专利权的责任。
Any trade name used in this document is information given for the convenience of users and does not constitute an endorsement.
本文件中使用的任何商号均为方便用户而提供的信息,并不构成对该商号的认可。
For an explanation of the voluntary nature of standards, the meaning of ISO specific terms and expressions related to conformity assessment, as well as information about ISO's adherence to the World Trade Organization (WTO) principles in the Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT), seewww.iso.org/iso/foreword.html.
关于标准的自愿性、与合格评定相关的ISO 特定术语和表达的含义,以及ISO 遵守世界贸易组织(WTO)《技术性贸易壁垒协定》(TBT)原则的信息,请参见 www.iso.org/iso/foreword.html。
This document was prepared by Technical Committee ISO/TC 176, Quality management and quality assurance, Subcommittee SC 2, Quality systems.
本文件由ISO/TC 176 技术委员会“质量管理和质量保证”的 SC 2 小组委员会“质量体系”制定。
This sixth edition cancels and replaces the fifth edition (ISO 9001:2015).
第六版取消并取代第五版(ISO 9001:2015)。
Introduction
引言
0.1 General
0.1 总则
The adoption of a quality management system is a strategic decision for an organization that can help to improve its overall performance and provide a sound basis for sustainable development initiatives.
采用质量管理体系是组织的一项战略性决策,有助于改进其整体绩效,并为可持续发展倡议提供坚实的基础。
The potential benefits to an organization of implementing a quality management system based on the requirements in this document are:
组织基于本文件要求实施质量管理体系的潜在收益是:
a) the ability to consistently provide products and services that meet customer and applicable statutory and regulatory requirements;
a) 稳定地提供满足顾客和适用的法律法规要求的产品和服务的能力;
b) facilitating opportunities to enhance customer satisfaction;
b) 促进增强顾客满意的机会;
c) addressing risks and opportunities associated with its context and objectives;
c) 应对与其环境和目标相关的风险和机遇;
d) the ability to demonstrate conformity to specified quality management system requirements.
d) 证实符合规定的质量管理体系要求的能力。
This document can be used by internal and external parties.
本文件可供内部和外部各方使用。
It is not the intent of this document to imply the need for:
本文件无意要求:
— uniformity in the structure of different quality management systems;
— 不同质量管理体系在结构上的统一;
— alignment of documentation to the clause structure of this document;
— 文件与本文件的条款结构保持一致;
— the use of the specific terminology of this document within the organization.
— 在组织内部使用本文件的特定术语。
The quality management system requirements specified in this document are complementary to requirements for products and services.
本文件中规定的质量管理体系要求是对产品和服务要求的补充。
Consistently meeting requirements and addressing future needs and expectations of customers and relevant interested parties poses a challenge for organizations in an increasingly dynamic and complex environment. To achieve this objective, the organization can adopt various forms of improvement in addition to continual improvement, such as breakthrough change, innovation and reorganization.
在日益动态和复杂的环境中,持续满足要求并应对顾客及相关方的未来需求和期望对组织构成了挑战。为实现此目标,组织除了持续改进外,还可以采取各种形式的改进,如突破性变革、创新和重组。
In this document, the following verbal forms are used:
本文件中使用以下助动词:
— “shall” indicates a requirement;
— “应”表示要求;
— “should” indicates a recommendation;
— “宜”表示建议;
— “may” indicates a permission;
— “可”表示允许;
— “can” indicates a possibility or a capability.
— “能”表示可能性或能力。
Information marked as “NOTE” is for guidance in understanding or clarifying the associated requirement.
标注为“注”的信息是为了帮助理解或澄清相关要求。
Annex A provides information and clarifications that can support understanding of the requirements of this document. This is an informative annex and does not contain any additional requirements.
附录A提供了有助于理解本文件要求的信息和说明。这是一个资料性附录,不包含任何附加要求。
The explanatory information is given only on clauses needing clarification.
解释性信息仅针对需要澄清的条款给出。
For guidance on the application of all clauses in this document see ISO/TS 9002[1].
关于本文件所有条款的应用指南,请参见ISO/TS 9002[1]。
0.2 Quality management principles
0.2 质量管理原则
This document is based on the quality management principles described in ISO/CD 9000. The descriptions include a statement of each principle, a rationale of why the principle is important for the organization, some examples of benefits associated with the principle and examples of typical actions to improve the organization's performance when applying the principle.
本文件基于ISO/CD 9000中所述的质量管理原则。这些描述包括每项原则的陈述、该原则对组织重要性的原理、与该原则相关的一些收益示例,以及应用该原则时改进组织绩效的典型措施示例。
The quality management principles are:
质量管理原则是:
— customer focus;
— 以顾客为关注焦点;
— leadership;
— 领导作用;
— engagement of people;
— 全员参与;
— process approach;
— 过程方法;
— improvement;
— 改进;
— evidence-based decision making;
— 循证决策;
— relationship management.
— 关系管理。
0.3 Process approach
0.3 过程方法
0.3.1 General
0.3.1 总则
This document promotes the adoption of a process approach when establishing, implementing and improving the effectiveness of a quality management system, to enhance customer satisfaction by meeting customer requirements. Specific requirements considered essential to the adoption of a process approach are included in 4.4.
本文件提倡在建立、实施和改进质量管理体系有效性时采用过程方法,通过满足顾客要求来增强顾客满意。采用过程方法所必需的具体要求包含在4.4中。
Understanding and managing interrelated processes as a system contributes to the organization's effectiveness and efficiency in achieving its intended results. This approach enables the organization to control the interrelationships and interdependencies among the processes of the system, so that the overall performance of the organization can be enhanced.
将相互关联的过程作为一个体系来理解和管理,有助于组织有效和高效地实现其预期结果。这种方法使组织能够控制体系中过程之间的相互关系和相互依赖性,从而提升组织的整体绩效。
The process approach involves the systematic determination and management of processes, and their interactions, so as to achieve the intended results in accordance with the quality policy and strategic direction of the organization. Management of the processes and the system as a whole can be achieved using the PDCA cycle (see 0.3.2) with an overall focus on risk-based thinking (see A.6.1.2) and opportunity-based thinking (see A.6.1.3) aimed at taking advantage of opportunities and preventing undesirable results.
过程方法涉及对过程及其相互作用的系统性确定和管理,以便根据组织的质量方针和战略方向实现预期结果。整个过程和体系的管理可以通过PDCA循环(见0.3.2)实现,并整体关注旨在利用机遇和预防不良结果的基于风险的思维(见A.6.1.2)和基于机遇的思维(见A.6.1.3)。
The application of the process approach in a quality management system enables:
在质量管理体系中应用过程方法能够:
a) understanding and consistency in meeting requirements;
a) 理解并持续地满足要求;
b) the consideration of processes in terms of added value;
b) 从增值的角度考虑过程;
c) the achievement of effective process performance;
c) 实现有效的过程绩效;
d) improvement of processes based on the results of evaluation of data and information.
d) 基于数据和信息的评价结果改进过程。
Figure 1 gives a schematic representation of any process and shows the interaction of its elements. The monitoring and measuring check points, which are necessary for control, are specific to each process and will vary depending on the process steps and related risks.
图1示意性地表示了任何过程,并展示了其要素的相互作用。控制所需的监视和测量检查点是针对每个过程特定的,并将根据过程步骤和相关风险而变化。
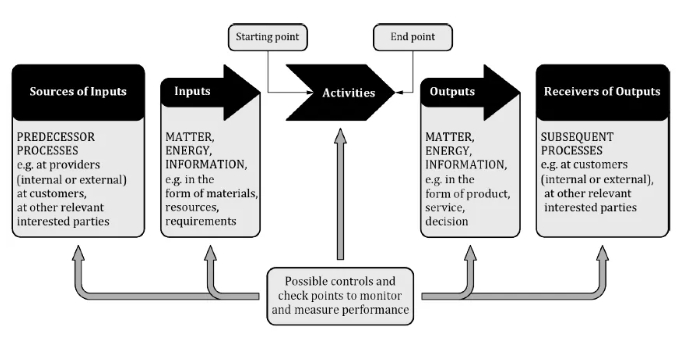
Figure 1 — Schematic representation of the elements of a single process
图1 — 单一过程要素示意图
0.3.2 Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle
0.3.2 策划-实施-检查-处置(PDCA)循环
The PDCA cycle can be applied to all processes and to the quality management system as a whole. Figure 2 illustrates how Clause 4 to Clause 10 of this document can be grouped in relation to the PDCA cycle.
PDCA循环可以应用于所有过程以及整个质量管理体系。图2说明了本文件第4章至第10章如何与PDCA循环相关联地进行分组。
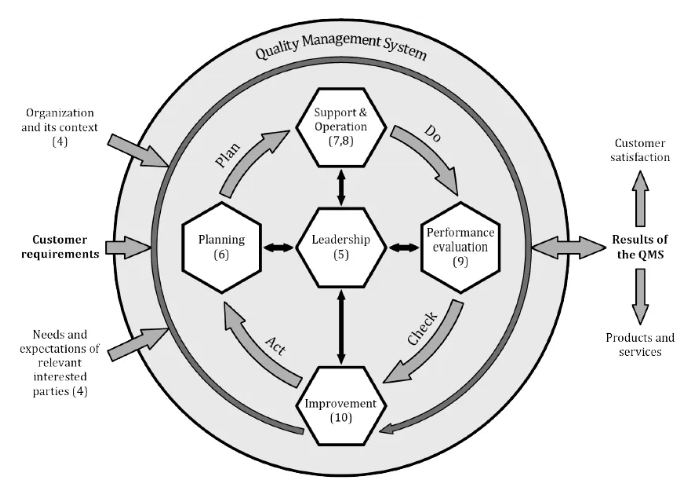
NOTE Numbers in brackets refer to the clauses in this document.
注:括号中的数字指本文件中的条款。
Figure 2 — Representation of the structure of this document in the PDCA cycle
图2 — 本文件在PDCA循环中的结构表示
The PDCA cycle can be briefly described as follows:
PDCA循环可简述如下:
— Plan: establish the objectives of the system and its processes, and the resources needed to deliver results in accordance with customers' requirements and the organization's policies, and determine and address risks and opportunities;
— 策划(Plan):根据顾客的要求和组织的方针,建立体系及其过程的目标,并确定交付结果所需的资源,以及确定和应对风险与机遇;
— Do: implement what was planned;
— 实施(Do):实施所策划的内容;
— Check: monitor and (where applicable) measure processes and the resulting products and services against policies, objectives, requirements and planned activities, and report the results;
— 检查(Check):根据方针、目标、要求和策划的活动,监视并(适用时)测量过程以及产生的产品和服务,并报告结果;
— Act: take actions to improve performance, as necessary.
— 处置(Act):必要时,采取措施以改进绩效。
0.4 Relationship with other management system standards
0.4 与其他管理体系标准的关系
This document applies the harmonized structure to improve alignment among ISO management systems standards.
本文件应用了协调结构,以改进ISO管理体系标准之间的一致性。
This document enables an organization to use the process approach, coupled with the PDCA cycle, risk-based thinking and opportunity-based thinking, to align or integrate its quality management system with the requirements of other management system standards.
本文件使组织能够运用过程方法,并结合PDCA循环、基于风险的思维和基于机遇的思维,使其质量管理体系与其他管理体系标准的要求相协调或整合。
This document relates to :
本文件与以下文件相关:
— ISO/CD 9000 Quality management systems — Fundamentals and vocabulary provides essential background for the proper understanding and implementation of this document;
— ISO/CD 9000《质量管理体系— 基础和术语》为正确理解和实施本文件提供了必要的基础;
— ISO 9004[2] Quality management – Quality of an organization – Guidance to achieve sustained success provides guidance for organizations that choose to progress beyond the requirements of this document.
— ISO 9004[2]《质量管理— 组织质量— 获得持续成功的指南》为那些选择超越本文件要求并谋求发展的组织提供了指南。
— ISO/TS 9002[1] Quality management systems – Guidelines for the application of ISO 9001 provides implementation guidance.
— ISO/TS 9002[1]《质量管理体系— ISO 9001应用指南》提供了实施指南。
This document does not include requirements specific to other management systems, such as those for environmental management, occupational health and safety management, or financial management.
本文件不包括针对其他管理体系的特定要求,例如环境管理、职业健康安全管理或财务管理。
Sector-specific ISO quality management system standards based on the requirements of this document have been developed. Some of these standards specify additional quality management system requirements, while others are limited to providing guidance to the application of this document within the particular sector.
基于本文件要求,已制定了特定行业的ISO质量管理体系标准。其中一些标准规定了额外的质量管理体系要求,而另一些则仅限于在特定行业内为本文件的应用提供指南。
NOTE Seehttps://www.iso.org/management-system-standards-list.html[3] for a list of all management system standards.
注:所有管理体系标准的列表见 https://www.iso.org/management-system-standards-list.html[3]。
DRAFT International Standard
国际标准草案
Quality management systems — Requirements
质量管理体系— 要求
1 Scope
1 范围
This document specifies requirements for a quality management system when an organization:
本文件为组织在下列情况下规定了对质量管理体系的要求:
a) needs to demonstrate its ability to consistently provide products and services that meet customer and applicable statutory and regulatory requirements, and
a) 需要证实其具有稳定地提供满足顾客要求和适用法律法规要求的产品和服务的能力,以及
b) aims to enhance customer satisfaction through the effective application of the system, including processes for improvement of the system and the assurance of conformity to customer and applicable statutory and regulatory requirements.
b) 旨在通过体系的有效应用,包括体系改进的过程,以及确保持续符合顾客和适用的法律法规要求,以增强顾客满意。
All the requirements of this document are generic.
本文件的所有要求都是通用的。
This document is applicable to any organization, regardless of its type or size, or the products and services it provides.
本文件适用于任何类型、任何规模、提供任何产品和服务的组织。
NOTE 1 In this document, the terms "product" or "service" only apply to products and services intended for, or required by, a customer.
注1:在本文件中,术语“产品”或“服务”仅适用于为顾客提供或顾客要求的产品和服务。
NOTE 2 Statutory and regulatory requirements can be expressed as legal requirements.
注2:法律法规要求可表述为法定要求。
2 Normative references
2 规范性引用文件
The following documents are referred to in the text in such a way that some or all of their content constitutes requirements of this document. For dated references, only the edition cited applies. For undated references, the latest edition of the referenced document (including any amendments) applies.
下列文件中的条款通过在本文件中的引用而构成本文件的条款。凡是注日期的引用文件,仅该日期版本适用于本文件。凡是不注日期的引用文件,其最新版本(包括所有的修改单)适用于本文件。
ISO/CD 9000, Quality management systems — Fundamentals and vocabulary
ISO/CD 9000, 质量管理体系— 基础和术语
3 Terms and definitions
3 术语和定义
For the purposes of this document, the terms and definitions given in ISO/CD 9000 including the following apply.
为本文件的目的,采用ISO/CD 9000给出的术语和定义以及下列术语和定义。
ISO and IEC maintain terminology databases for use in standardization at the following addresses: • ISO Online browsing platform: available athttps://www.iso.org/obp
ISO和IEC在以下地址维护用于标准化的术语数据库:
• ISO在线浏览平台:https://www.iso.org/obp
• IEC Electropedia: available athttps://www.electropedia.org
• IEC电工百科:https://www.electropedia.org
3.1
organization
组织
person or group of people that has its own functions with responsibilities, authorities and relationships to achieve its objectives (3.6)
为实现其目标(3.6),由具备职责、权限和相互关系的个人或一组人构成的实体。
Note 1 to entry: The concept of organization includes, but is not limited to, sole-trader, company, corporation, firm, enterprise, authority, partnership, charity or institution, or part or combination thereof, whether incorporated or not, public or private.
注1:组织的概念包括但不限于:独资企业、公司、集团、商行、企事业单位、政府机构、合伙企业、慈善机构或社团,或上述组织的部分或组合,无论其是否注册,是公有还是私有。
Note 2 to entry: If the organization is part of a larger entity, the term “organization” refers only to the part of the larger entity that is within the scope of the quality management system (3.4.1).
注2:如果组织是某个更大实体的一部分,术语“组织”仅指该更大实体中处于质量管理体系(3.4.1)范围内的那一部分。
3.2
interested party
相关方
stakeholder
利益相关方
person or organization (3.1) that can affect, be affected by, or perceive itself to be affected by a decision or activity
能够影响决策或活动,或被决策或活动所影响,或自认为被决策或活动所影响的个人或组织(3.1)。
EXAMPLE Customers, owners, people in an organization, providers, bankers, regulators, unions, partners or society that can include competitors or opposing pressure groups.
示例:顾客、所有者、组织内人员、提供方、银行、监管机构、工会、合作伙伴或社会团体,其中可包括竞争者或持反对意见的压力集团。
3.3
top management
最高管理者
person or group of people who directs and controls an organization (3.1) at the highest level
在最高层指挥和控制组织(3.1)的一个人或一组人。
Note 1 to entry: Top management has the power to delegate authority and provide resources within the organization.
注1:最高管理者有权在组织内授权并提供资源。
Note 2 to entry: If the scope of the management system (3.4) covers only part of an organization, then top management refers to those who direct and control that part of the organization.
注2:如果管理体系(3.4)的范围仅覆盖组织的一部分,则最高管理者是指挥和控制该部分组织的那些人员。
3.4
management system
管理体系
set of interrelated or interacting elements of an organization (3.1) to establish policies (3.5) and objectives (3.6), as well as processes (3.8) to achieve those objectives
组织(3.1)中为建立方针(3.5)和目标(3.6)以及实现这些目标的过程(3.8)而相互关联或相互作用的一组要素。
Note 1 to entry: A management system can address a single discipline or several disciplines.
注1:一个管理体系可涉及单个或多个领域。
Note 2 to entry: The management system elements include the organization's structure, roles and responsibilities, planning and operation.
注2:管理体系的要素包括组织的结构、角色和职责、策划和运行。
Note 3 to entry: The management system elements can include the organization's policies, practices, rules, and beliefs.
注3:管理体系的要素可包括组织的方针、惯例、规则和理念。
Note 4 to entry: An organization manages its interrelated elements in an orderly manner to achieve its objectives.
注4:一个组织以有序的方式管理其相互关联的要素以实现其目标。
Note 5 to entry: The scope of a management system can include the whole of the organization, specific and identified functions of the organization, specific and identified sections of the organization, or one or more functions across a group of organizations.
注5:管理体系的范围可包括整个组织、组织中特定的和已识别的职能、组织中特定的和已识别的部门,或跨组织集团的一个或多个职能。
3.4.1
quality management system
质量管理体系
part of a management system (3.4) related to quality
管理体系(3.4)中与质量相关的部分。
3.5
policy
方针
intentions and direction of an organization (3.1) as formally expressed by its top management (3.3)
由最高管理者(3.3)正式发布的组织(3.1)的意图和方向。
3.5.1
quality policy
质量方针
policy (3.5) related to quality
与质量相关的方针(3.5)。
Note 1 to entry: The quality policy is generally consistent with the overall policy of the organization (3.1), can be aligned with the organization's vision and mission and provides a framework for the setting of quality objectives (3.6.1).
注1:质量方针通常与组织(3.1)的总体方针保持一致,可与组织的愿景和使命相协调,并为设定质量目标(3.6.1)提供一个框架。
Note 2 to entry: Quality management principles presented in ISO/CD 9000 can form a basis for the establishment of a quality policy.
注2:ISO/CD 9000中阐述的质量管理原则可作为建立质量方针的基础。
3.6
objective
目标
result to be achieved
要实现的结果。
Note 1 to entry: An objective can be strategic, tactical, or operational.
注1:目标可以是战略性的、战术性的或操作性的。
Note 2 to entry: Objectives can relate to different disciplines (such as finance, health and safety, and environment). They can be, for example, organization-wide or specific to a project, product, service, or process (3.8).
注2:目标可涉及不同领域(如财务、健康与安全、环境)。例如,它们可以是整个组织的,或是特定于某个项目、产品、服务或过程(3.8)的。
Note 3 to entry: An objective can be expressed in other ways, e.g. as an intended result, as a purpose, as an operational criterion, as a quality objective (3.6.1)or by the use of other words with similar meaning (e.g. aim, goal, or target).
注3:目标可以用其他方式来表达,例如,作为预期结果、目的、运行准则、质量目标(3.6.1),或使用其他具有类似含义的词语(如目的、宗旨或指标)。
Note 4 to entry: In the context of quality management system (3.4.1), quality objectives (3.6.1) are set by the organization (3.1), consistent with the quality policy (3.5.1), to achieve specific results.
注4:在质量管理体系(3.4.1)的背景下,质量目标(3.6.1)由组织(3.1)设定,与质量方针(3.5.1)保持一致,以实现特定的结果。
3.6.1
quality objective
质量目标
objective (3.6) related to quality
与质量相关的目标(3.6)。
Note 1 to entry: Quality objectives are generally based on the organization's (3.1) quality policy (3.5.1).
注1:质量目标通常基于组织(3.1)的质量方针(3.5.1)。
Note 2 to entry: Quality objectives are generally specified for relevant functions, levels and processes (3.8) in the organization.
注2:质量目标通常在组织的相关职能、层次和过程(3.8)中被规定。
3.7
risk
风险
effect of uncertainty
不确定性的影响。
Note 1 to entry: An effect is a deviation from the expected — positive or negative.
注1:影响是一种偏离预期的结果——可能是积极的,也可能是消极的。
Note 2 to entry: Uncertainty is the state, even partial, of deficiency of information related to, understanding or knowledge of an event, its consequence, or likelihood.
注2:不确定性是指,在对某个事件、其后果或其可能性的信息、理解或知识方面存在缺乏的状态,哪怕是部分缺乏。
Note 3 to entry: risk (3.7) is often characterized by reference to potential events and consequences or a combination of these.
注3:风险(3.7)通常通过参照潜在的事件和后果,或其组合来描述。
Note 4 to entry: Risk is often expressed in terms of a combination of the consequences of an event (including changes in circumstances) and the associated likelihood of occurrence.
注4:风险通常表示为事件后果(包括环境变化)与相关发生可能性的组合。
Note 5 to entry: The word "risk" is sometimes used when there is the possibility of only negative consequences.
注5:“风险”一词有时用于仅存在负面后果可能性之时。
3.8
process
过程
set of interrelated or interacting activities that uses or transforms inputs to deliver a result
利用或转换输入以交付结果的一组相互关联或相互作用的活动。
Note 1 to entry: Whether the result of a process is called an output, a product or a service depends on the context of the reference.
注1:一个过程的结果是称为输出、产品还是服务,取决于其引用的语境。
Note 2 to entry: Inputs to a process are generally the outputs of other processes and outputs of a process are generally the inputs to other processes.
注2:一个过程的输入通常是其他过程的输出,而一个过程的输出通常是其他过程的输入。
Note 3 to entry: Two or more interrelated and interacting processes in series can also be referred to as a process.
注3:两个或多个串联的相互关联和相互作用的过程也可以称为一个过程。
Note 4 to entry: Processes in an organization (3.1) are generally planned and carried out under controlled conditions to ensure that intended results can be achieved.
注4:组织(3.1)中的过程通常是在受控条件下策划和执行的,以确保能够实现预期结果。
Note 5 to entry: A process where the conformity (3.15) of the resulting output cannot be readily or economically validated is frequently referred to as a "special process".
注5:结果输出的符合性(3.15)无法被便捷或经济地验证的过程,通常被称为“特殊过程”。
3.9
competence
能力
ability to apply knowledge and skills to achieve intended results
应用知识和技能以实现预期结果的本领。
Note 1 to entry: Demonstrated competence is sometimes referred to as qualification.
注1:被证实的能力有时被称为资格。
3.10
documented information
形成文件的信息
information required to be controlled and maintained by an organization (3.1) and the medium on which it is contained
组织(3.1)需要控制和维护的信息及其载体。
Note 1 to entry: Documented information can be in any format and media and from any source.
注1:形成文件的信息可以任何格式和媒介存在,并可来自任何来源。
Note 2 to entry: Documented information can refer to:
注2:形成文件的信息可涉及:
— the management system (3.4), including related processes (3.8);
— 管理体系(3.4),包括相关过程(3.8);
— information created in order for the organization to operate (documentation);
— 为组织运行而创建的信息(文件);
— evidence of results achieved (records).
— 所取得结果的证据(记录)。
3.11
performance
绩效
measurable result
可测量的结果。
Note 1 to entry: Performance can relate either to quantitative or qualitative findings.
注1:绩效可以与定量的或定性的发现相关。
Note 2 to entry: Performance can relate to managing activities, processes (3.8), products, services, systems or organizations (3.1).
注2:绩效可以与管理活动、过程(3.8)、产品、服务、体系或组织(3.1)相关。
3.12
continual improvement
持续改进
recurring activity to enhance performance (3.11)
为提升绩效(3.11)而反复进行的活动。
3.13
effectiveness
有效性
extent to which planned activities are realized and planned results are achieved
策划的活动得以实现和策划的结果得以达成的程度。
3.14
requirement
要求
need or expectation that is stated, generally implied or obligatory
明示的、通常隐含的或必须履行的需求或期望。
Note 1 to entry: "Generally implied" means that it is custom or common practice for the organization (3.1) and interested party (3.2) that the need or expectation under consideration is implied.
注1:“通常隐含的”是指,对于组织(3.1)和相关方(3.2)来说,所考虑的需求或期望是不言而喻的惯例或常规做法。
Note 2 to entry: A specified requirement is one that is stated, e.g. in documented information (3.10).
注2:规定的要求是明示的要求,例如,在形成文件的信息(3.10)中陈述的要求。
Note 3 to entry: A qualifier can be used to denote a specific type of requirement, e.g. product requirement, service requirement, quality management requirement, customer requirement, quality requirement.
注3:可使用限定词来表示特定类型的要求,例如,产品要求、服务要求、质量管理要求、顾客要求、质量要求。
Note 4 to entry: Requirements can be generated by different interested parties or by the organization itself.
注4:要求可由不同的相关方或由组织自身提出。
3.15
conformity
符合
fulfilment of a requirement (3.14)
对一项要求(3.14)的满足。
Note 1 to entry: In English the word "conformance" is synonymous but deprecated. In French the word "compliance" is synonymous but deprecated.
注1:在英语中,“conformance”一词是同义词但已不推荐使用。在法语中,“compliance”一词是同义词但已不推荐使用。
3.16
nonconformity
不符合
non-fulfilment of a requirement (3.14)
对一项要求(3.14)的未满足。
3.17
corrective action
纠正措施
action to eliminate the cause(s) of a nonconformity (3.16) and to prevent recurrence
为消除一个不符合(3.16)的原因并防止其再发生所采取的措施。
Note 1 to entry: There can be more than one cause for a nonconformity.
注1:一个不符合可能有一个以上的原因。
Note 2 to entry: Corrective action is taken to prevent recurrence whereas preventive action is taken to prevent occurrence.
注2:采取纠正措施是为了防止再发生,而采取预防措施是为了防止发生。
3.18
audit
审核
systematic and independent process (3.8) for obtaining evidence and evaluating it objectively to determine the extent to which the audit criteria are fulfilled
为获得证据并对其进行客观评价,以确定审核准则被满足的程度所进行的系统的、独立的并且形成文件的过程(3.8)。
Note 1 to entry: An audit can be an internal audit (first party) or an external audit (second party or third party), and it can be a combined audit (combining two or more disciplines).
注1:审核可以是内部审核(第一方)或外部审核(第二方或第三方),也可以是结合审核(合并两个或多个领域)。
Note 2 to entry: An internal audit is conducted by the organization (3.1) itself, or by an external party on its behalf.
注2:内部审核由组织(3.1)自己进行,或由外部方代表其进行。
Note 3 to entry: "Audit evidence" and "audit criteria" are defined in ISO 19011.
注3:“审核证据”和“审核准则”在ISO 19011中有定义。
Note 4 to entry: The fundamental elements of an audit include the determination of the conformity (3.15) of an object according to a procedure carried out by people selected to ensure impartiality and objectivity of the audit process.
注4:审核的基本要素包括,根据由被选定以确保审核过程公正客观的人员所执行的程序,来确定一个对象的符合性(3.15)。
Note 5 to entry: Internal audits are conducted for management review and other internal purposes and can form the basis for an organization's declaration of conformity. Independence can be demonstrated by the freedom from responsibility for the activity being audited.
注5:内部审核为管理评审和其他内部目的而进行,并可构成组织符合性声明的基础。独立性可通过审核员独立于受审核活动的职责来证明。
Note 6 to entry: Second party audits are conducted by parties having an interest in the organization, such as customers, or by other persons on their behalf. Third-party audits are conducted by external, independent auditing organizations such as those providing certification/registration of conformity or governmental agencies.
注6:第二方审核由对组织有利害关系的各方(如顾客)或由其代表进行。第三方审核由外部独立的审核组织(如提供符合性认证/注册的机构或政府机构)进行。
Note 7 to entry: An audit can also be a joint audit carried out by two or more auditing organizations.
注7:审核也可以是由两个或多个审核组织进行的联合审核。
3.19
measurement
测量
process (3.8) to determine a value
确定一个值的过程(3.8)。
Note 1 to entry: According to ISO 3534-2, 3.2.1, the value determined is generally the value of a quantity.
注1:根据ISO 3534-2, 3.2.1,所确定的值通常是一个量值。
3.20
monitoring
监视
determining the status of a system, a process (3.8) or an activity
确定一个体系、一个过程(3.8)或一项活动的状态。
Note 1 to entry: To determine the status, there can be a need to check, supervise or critically observe.
注1:为确定状态,可能需要检查、监督或严格观察。
Note 2 to entry: Monitoring can also determine the status of a product or a service.
注2:监视也可以确定一个产品或服务的状态。
Note 3 to entry: Monitoring is generally a determination of the status of an object carried out at different stages or at different times.
注3:监视通常是在不同阶段或不同时间对一个对象状态的确定。
4 Context of the organization
4 组织环境
4.1 Understanding the organization and its context
4.1 理解组织及其环境
The organization shall determine external and internal issues that are relevant to its purpose and its strategic direction and that affect its ability to achieve the intended result(s) of its quality management system.
组织应确定与其宗旨和战略方向相关并影响其实现质量管理体系预期结果能力的外部和内部因素。
The organization shall determine whether climate change is a relevant issue.
组织应确定气候变化是否是一个相关因素。
The organization shall monitor and review information about these external and internal issues.
组织应对这些外部和内部因素的相关信息进行监视和评审。
NOTE 1 Issues can include positive and negative factors or conditions for consideration.
注1:因素可包括需要考虑的积极和消极的要素或条件。
NOTE 2 Understanding the external context can be facilitated by considering legal, technological, competitive, market, cultural, political, social, economic and environmental issues, whether international, national, regional or local.
注2:通过考虑法律、技术、竞争、市场、文化、政治、社会、经济和环境等问题(无论是国际、国家、地区还是地方层面),可以促进对外部环境的理解。
NOTE 3 Understanding the internal context can be facilitated by considering issues related to the organization's strategic direction, values, culture, resources, knowledge and performance.
注3:通过考虑与组织的战略方向、价值观、文化、资源、知识和绩效相关的问题,可以促进对内部环境的理解。
4.2 Understanding the needs and expectations of interested parties
4.2 理解相关方的需求和期望
The organization shall determine:
组织应确定:
a) the interested parties that are relevant to the quality management system;
a) 与质量管理体系相关的相关方;
b) the relevant requirements of these interested parties;
b) 这些相关方的相关要求;
c) which of these requirements will be addressed through the quality management system.
c) 这些要求中的哪些将通过质量管理体系来应对。
The organization shall monitor and review information about these interested parties and their relevant requirements.
组织应监视和评审有关这些相关方及其相关要求的信息。
NOTE Relevant interested parties can have requirements related to climate change.
注:相关方可能对气候变化有相关要求。
4.3 Determining the scope of the quality management system
4.3 确定质量管理体系的范围
The organization shall determine the boundaries and applicability of the quality management system to establish its scope.
组织应确定质量管理体系的边界和适用性,以建立其范围。
When determining this scope, the organization shall consider:
在确定此范围时,组织应考虑:
a) the external and internal issues referred to in 4.1;
a) 4.1中提及的外部和内部因素;
b) the requirements referred to in 4.2;
b) 4.2中提及的要求;
c) the products and services of the organization.
c) 组织的产品和服务。
The scope shall state the types of products and services covered, and provide justification for any requirement of this document that the organization determines is not applicable to its quality management system.
范围应说明所覆盖的产品和服务类型,并对组织确定不适用于其质量管理体系的本文件任何要求提供理由。
The organization shall apply all the requirements of this document if they are applicable within the determined scope of its quality management system.
如果本文件的所有要求在确定的质量管理体系范围内适用,组织应应用这些要求。
The scope shall be available as documented information.
范围应作为形成文件的信息予以保持。
Conformity to this document can only be claimed if the requirements determined as not being applicable do not affect the organization's ability or responsibility to ensure the conformity of its products and services and the enhancement of customer satisfaction.
只有在确定为不适用的要求不影响组织确保其产品和服务符合性以及增强顾客满意的能力或责任时,才能声称符合本文件。
4.4 Quality management system
4.4 质量管理体系
4.4.1 The organization shall establish, implement, maintain and continually improve a quality management system, including the processes needed and their interactions, in accordance with the requirements of this document.
4.4.1 组织应根据本文件的要求,建立、实施、保持和持续改进质量管理体系,包括所需的过程及其相互作用。
The organization shall determine the processes needed for the quality management system and their application throughout the organization, and shall:
组织应确定质量管理体系所需的过程及其在整个组织中的应用,并应:
a) determine the inputs required and the outputs expected from these processes;
a) 确定这些过程所需的输入和期望的输出;
b) determine the sequence and interaction of these processes;
b) 确定这些过程的顺序和相互作用;
c) determine and apply the criteria and methods (including monitoring, measurements and related performance indicators) needed to ensure the effective operation and control of these processes;
c) 确定并应用确保这些过程有效运行和控制所需的准则和方法(包括监视、测量和相关的绩效指标);
d) determine the resources needed for these processes and ensure their availability;
d) 确定这些过程所需的资源并确保其可用性;
e) assign the responsibilities and authorities for these processes;
e) 为这些过程分配职责和权限;
f) address the risks and opportunities as determined in accordance with the requirements of 6.1;
f) 按照6.1的要求应对所确定的风险和机遇;
g) evaluate these processes and implement any changes needed to ensure that these processes achieve their intended results;
g) 评价这些过程并实施任何必要的变更,以确保这些过程实现其预期结果;
h) improve the processes and the quality management system.
h) 改进过程和质量管理体系。
4.4.2 Documented information shall be available to the extent necessary:
4.4.2 应在必要范围内提供形成文件的信息:
a) to support the operation of its processes;
a) 以支持其过程的运行;
b) as evidence that the processes are being carried out as planned.
b) 作为过程按策划实施的证据。
5 Leadership
5 领导作用
5.1 Leadership and commitment
5.1 领导作用和承诺
5.1.1 General
5.1.1 总则
Top management shall demonstrate leadership and commitment with respect to the quality management system by:
最高管理者应通过以下方面,证实其在质量管理体系方面的领导作用和承诺:
a) ensuring that the quality policy and quality objectives are established and are compatible with the strategic direction of the organization;
a) 确保质量方针和质量目标得以建立,并与组织的战略方向相一致;
b) ensuring the integration of the quality management system requirements into the organization's business processes;
b) 确保将质量管理体系的要求融入组织的业务过程;
c) ensuring that the resources needed for the quality management system are available;
c) 确保质量管理体系所需的资源是可用的;
d) communicating the importance of effective quality management and of conforming to the quality management system requirements;
d) 沟通有效的质量管理以及符合质量管理体系要求的重要性;
e) ensuring that the quality management system achieves its intended results;
e) 确保质量管理体系实现其预期结果;
f) directing and supporting persons to contribute to the effectiveness of the quality management system;
f) 指导和支持员工为质量管理体系的有效性做出贡献;
g) promoting continual improvement;
g) 促进持续改进;
h) supporting other relevant roles to demonstrate their leadership as it applies to their areas of responsibility;
h) 支持其他相关管理岗位展示其在其职责领域内的领导作用;
i) promoting quality culture and ethical behaviour;
i) 倡导质量文化和道德行为;
j) promoting the use of the process approach and risk-based thinking;
j) 倡导使用过程方法和基于风险的思维;
k) taking accountability for the effectiveness of the quality management system.
k) 对质量管理体系的有效性承担责任。
NOTE 1 Reference to "business" in this document can be interpreted broadly to mean those activities that are core to the purposes of the organization's existence.
注1:本文件中提及的“业务”可被广义地解释为对组织存在目的至关重要的那些活动。
NOTE 2 An organization's quality culture and ethical behaviour are reflected in its shared values, attitudes, and established practices.
注2:一个组织的质量文化和道德行为体现在其共同的价值观、态度和既定惯例中。
5.1.2 Customer focus
5.1.2 以顾客为关注焦点
Top management shall demonstrate leadership and commitment with respect to customer focus by ensuring that:
最高管理者应通过确保以下方面,证实其在以顾客为关注焦点方面的领导作用和承诺:
a) customer and applicable statutory and regulatory requirements are determined, understood and consistently met;
a) 确定、理解并持续满足顾客要求和适用的法律法规要求;
b) the risks and opportunities that can affect conformity of products and services and the ability to enhance customer satisfaction are determined and addressed;
b) 确定并应对可能影响产品和服务符合性以及增强顾客满意能力的风险和机遇;
c) the focus on enhancing customer satisfaction is maintained.
c) 保持对增强顾客满意的关注。
5.2 Quality policy
5.2 质量方针
5.2.1 Top management shall establish a quality policy that:
5.2.1 最高管理者应建立一项质量方针,该方针:
a) is appropriate to the purpose of the organization;
a) 与组织的宗旨相适应;
b) provides a framework for setting quality objectives;
b) 为设定质量目标提供框架;
c) includes a commitment to meet applicable requirements;
c) 包括满足适用要求的承诺;
d) includes a commitment to continual improvement of the quality management system;
d) 包括对持续改进质量管理体系的承诺;
e) takes into account the context of the organization and supports its strategic direction.
e) 考虑了组织的环境并支持其战略方向。
The quality policy shall be implemented and maintained.
质量方针应得到实施和保持。
5.2.2 The quality policy shall:
5.2.2 质量方针应:
a) be available as documented information;
a) 作为形成文件的信息予以保持;
b) be communicated within the organization;
b) 在组织内得到沟通;
c) be available to interested parties, as appropriate;
c) 适当时,可为相关方获取;
d) be understood and applied within the organization.
d) 在组织内得到理解和应用。
5.3 Roles, responsibilities and authorities
5.3 组织的角色、职责和权限
Top management shall ensure that the responsibilities and authorities for relevant roles are assigned, communicated and understood within the organization.
最高管理者应确保在组织内分配、沟通和理解相关岗位的职责和权限。
Top management shall assign the responsibility and authority for:
最高管理者应为下列事项分配职责和权限:
a) ensuring that the quality management system conforms to the requirements of this document;
a) 确保质量管理体系符合本文件的要求;
b) reporting on the performance of the quality management system to top management;
b) 向最高管理者报告质量管理体系的绩效;
c) ensuring that the processes are delivering their intended outputs;
c) 确保过程产出预期的输出;
d) ensuring the promotion of customer focus throughout the organization;
d) 确保在整个组织内提升以顾客为关注焦点的意识;
e) reporting on opportunities for improvement to top management;
e) 向最高管理者报告改进的机会;
f) ensuring that the integrity of the quality management system is maintained including when changes to the quality management system are planned and implemented.
f) 确保在策划和实施质量管理体系变更时,保持其完整性。
6 Planning
6 策划
6.1 Actions to address risks and opportunities
6.1 应对风险和机遇的措施
6.1.1 Determining risks and opportunities
6.1.1 确定风险和机遇
When planning for the quality management system, the organization shall consider the issues referred to in 4.1 and the requirements referred to in 4.2 and determine the risks and opportunities that need to be addressed to:
在策划质量管理体系时,组织应考虑4.1中所述的问题和4.2中所述的要求,并确定需要应对的风险和机遇,以便:
a) give assurance that the quality management system can achieve its intended result(s);
a) 确保质量管理体系能够实现其预期结果;
b) prevent, or reduce, undesired effects;
b) 预防或减少非预期的影响;
c) achieve continual improvement;
c) 实现持续改进;
d) enhance desirable effects.
d) 增强预期的影响。
6.1.2 Actions to address risks
6.1.2 应对风险的措施
The organization shall determine, analyse, and evaluate risks that can have an undesirable effect on its ability to continually and consistently provide conforming products and services and enhance customer satisfaction.
组织应确定、分析和评价可能对其持续稳定地提供合格产品和服务以及增强顾客满意的能力产生不良影响的风险。
The organization shall plan:
组织应策划:
a) actions to address these risks;
a) 应对这些风险的措施;
b) how to:
b) 如何:
1) integrate and implement the actions into its quality management system processes;
1) 将这些措施整合并实施到其质量管理体系过程中;
2) evaluate the effectiveness of these actions.
2) 评价这些措施的有效性。
Actions taken to address risks shall be proportionate to the potential impact on the conformity of products and services.
所采取的应对风险的措施应与对产品和服务符合性的潜在影响相适应。
NOTE 1 Determined risks can include risks related to the ability to provide conforming products and services during and after a disruption.
注1:确定的风险可包括在中断期间和之后提供合格产品和服务能力相关的风险。
NOTE 2 Actions to address risks can include avoiding risk, taking risk in order to pursue an opportunity, eliminating the risk source, changing the likelihood or consequences, sharing the risk, or retaining risk by informed decision.
注2:应对风险的措施可包括:规避风险、为寻求机遇而承担风险、消除风险源、改变可能性或后果、分担风险或通过知情决策保留风险。
6.1.3 Actions to address opportunities
6.1.3 应对机遇的措施
The organization shall determine, analyse, and evaluate opportunities that can have a desirable effect on its ability to continually and consistently provide conforming products and services and enhance customer satisfaction.
组织应确定、分析和评价可能对其持续稳定地提供合格产品和服务以及增强顾客满意的能力产生有利影响的机遇。
The organization shall plan:
组织应策划:
a) actions to address these opportunities;
a) 应对这些机遇的措施;
b) how to:
b) 如何:
1) integrate and implement the actions into its quality management system processes;
1) 将这些措施整合并实施到其质量管理体系过程中;
2) evaluate the effectiveness of these actions.
2) 评价这些措施的有效性。
Actions taken to address opportunities shall be proportionate to the potential impact on customer satisfaction and the conformity of products and services.
所采取的应对机遇的措施应与对顾客满意度和产品服务符合性的潜在影响相适应。
NOTE Actions to address opportunities can include adopting new practices, launching new products, creating new partnerships, leveraging new technologies, implementing initiatives and other actions to address the current and changing needs and expectations of its customers and other relevant interested parties.
注:应对机遇的措施可包括:采用新实践、推出新产品、建立新伙伴关系、利用新技术、实施新举措以及采取其他行动来应对其顾客和其他相关方当前和变化的需求与期望。
6.2 Quality objectives and planning to achieve them
6.2 质量目标及其实现的策划
6.2.1 The organization shall establish quality objectives at relevant processes, functions and levels.
6.2.1 组织应在相关过程、职能和层级上建立质量目标。
The quality objectives shall:
质量目标应:
a) be consistent with the quality policy;
a) 与质量方针保持一致;
b) be measurable;
b) 是可测量的;
c) take into account applicable requirements;
c) 考虑到适用的要求;
d) be monitored;
d) 得到监视;
e) be communicated;
e) 得到沟通;
f) be updated as appropriate;
f) 适当时予以更新;
g) be available as documented information;
g) 作为形成文件的信息予以保持;
h) be relevant to conformity of products and services and to enhancement of customer satisfaction.
h) 与产品和服务的符合性以及增强顾客满意相关。
6.2.2 When planning how to achieve its quality objectives, the organization shall determine:
6.2.2 在策划如何实现其质量目标时,组织应确定:
a) what will be done;
a) 要做什么;
b) what resources will be required;
b) 将需要什么资源;
c) who will be responsible;
c) 由谁负责;
d) when it will be completed;
d) 何时完成;
e) how the results will be evaluated.
e) 如何评价结果。
6.3 Planning of changes
6.3 变更的策划
When the organization determines the need for changes to the quality management system, the changes shall be carried out in a planned manner.
当组织确定需要对质量管理体系进行变更时,变更应以策划的方式进行。
To ensure changes are implemented effectively to achieve intended results the organization shall consider:
为确保变更得到有效实施以实现预期结果,组织应考虑:
a) the purpose of the changes and potential consequences;
a) 变更的目的及其潜在后果;
b) the integrity of the quality management system;
b) 质量管理体系的完整性;
c) the availability of resources and information;
c) 资源和信息的可用性;
d) the allocation or reallocation of responsibilities and authorities;
d) 职责和权限的分配或重新分配;
e) how the effectiveness of the changes will be monitored and evaluated;
e) 如何监视和评价变更的有效性;
f) communication of the changes;
f) 变更的沟通;
g) how to review the results of the changes.
g) 如何评审变更的结果。
7 Support
7 支持
7.1 Resources
7.1 资源
7.1.1 General
7.1.1 总则
The organization shall determine and provide the resources needed for the establishment, implementation, maintenance and continual improvement of the quality management system.
组织应确定并提供为建立、实施、保持和持续改进质量管理体系所需的资源。
The organization shall consider:
组织应考虑:
a) the capabilities of, and constraints on, existing internal resources;
a) 现有内部资源的能力和约束;
b) what needs to be obtained from external providers.
b) 需要从外部提供方获取什么。
7.1.2 People
7.1.2 人员
The organization shall determine and provide the persons necessary for the effective implementation of its quality management system and for the operation and control of its processes.
组织应确定并提供为有效实施其质量管理体系以及运行和控制其过程所需的人员。
7.1.3 Infrastructure
7.1.3 基础设施
The organization shall determine, provide and maintain the infrastructure necessary for the operation of its processes and to achieve conformity of products and services.
组织应确定、提供和维护其过程运行以及实现产品和服务符合性所需的基础设施。
NOTE For all types of work (e.g. on site, remote or a combination thereof) infrastructure can include:
注:对于所有类型的工作(例如现场、远程或其组合),基础设施可包括:
a) buildings and associated utilities;
a) 建筑物和相关设施;
b) equipment, including hardware and software;
b) 设备,包括硬件和软件;
c) transportation resources;
c) 运输资源;
d) information and communication technology.
d) 信息和通信技术。
7.1.4 Environment for the operation of processes
7.1.4 过程运行的环境
The organization shall determine, provide and maintain the environment necessary for the operation of its processes and to achieve conformity of products and services.
组织应确定、提供和维护其过程运行以及实现产品和服务符合性所需的环境。
NOTE A suitable environment can include a combination of factors, which can differ depending on the products and services provided. Relevant factors can include:
注:适宜的环境可包括多种因素的组合,这些因素会因所提供的产品和服务而异。相关因素可包括:
a) social (e.g. non-discriminatory, calm, non-confrontational);
a) 社会因素(例如,无歧视、安定、非对抗);
b) psychological (e.g. stress-reducing, burnout prevention, emotionally protective);
b) 心理因素(例如,减压、预防过度疲劳、稳定情绪);
c) physical (e.g. temperature, heat, humidity, light, airflow, hygiene, noise).
c) 物理因素(例如,温度、热度、湿度、光照、气流、卫生、噪音)。
Some factors are dependent on the organizational quality culture, including ethical behaviour.
一些因素取决于组织的质量文化,包括道德行为。
7.1.5 Monitoring and measuring resources
7.1.5 监视和测量资源
7.1.5.1 General
7.1.5.1 总则
The organization shall determine and provide the resources needed to ensure valid and reliable results when monitoring or measuring is used to verify the conformity of products and services to requirements.
当使用监视或测量来验证产品和服务与要求的符合性时,组织应确定并提供确保结果有效和可靠所需的资源。
The organization shall ensure that the resources provided:
组织应确保所提供的资源:
a) are suitable for the specific type of monitoring and measurement activities being undertaken;
a) 适用于所进行的特定类型的监视和测量活动;
b) are maintained to ensure their continuing fitness for their purpose.
b) 得到维护以确保其持续适用于其预期目的。
Appropriate documented information shall be available as evidence of fitness for purpose of the monitoring and measurement resources.
应提供适当的形成文件的信息,作为监视和测量资源适用其目的的证据。
7.1.5.2 Traceability of measurement results
7.1.5.2 测量结果溯源
When traceability of measurement results is a requirement, or is considered by the organization to be an essential part of providing confidence in the validity of measurement results, measuring equipment shall be:
当要求测量结果溯源时,或组织认为测量结果溯源是信任测量结果有效性的基础时,测量设备应:
a) calibrated or verified, or both, at specified intervals, or prior to use, against measurement standards traceable to international or national measurement standards; when no such standards exist, the basis used for calibration or verification shall be available as documented information;
a) 在规定时间间隔或使用前,依据可溯源到国际或国家测量标准的测量标准进行校准和(或)检定;当不存在此类标准时,用于校准或检定的依据应作为形成文件的信息予以保持;
b) identified in order to determine its calibration or verification status;
b) 得到识别,以确定其校准或检定状态;
c) safeguarded from adjustments, damage or deterioration that can invalidate measurement results.
c) 得到防护,以防止由于调整、损坏或衰减从而导致测量结果失效。
When measuring equipment is found to be unfit for its intended purpose, the organization shall determine whether the validity of previous measurement results has been adversely affected and shall take appropriate action as necessary.
当发现测量设备不适用于其预期目的时,组织应确定以往测量结果的有效性是否已受到不利影响,并应在必要时采取适当措施。
7.1.6 Organizational knowledge
7.1.6 组织知识
The organization shall determine the knowledge necessary for the operation of its processes and to achieve the intended results of its quality management system.
组织应确定其过程运行和实现其质量管理体系预期结果所需的知识。
This knowledge shall be retained, applied and shared to the extent necessary.
这些知识应在必要范围内予以保留、应用和共享。
When addressing changing needs and trends, the organization shall consider its current knowledge and determine how to acquire or access any necessary additional knowledge and required updates.
在应对变化的需求和趋势时,组织应考虑其现有知识,并确定如何获取或获得任何必要的额外知识和所需的更新。
NOTE Sources of organizational knowledge can include: experience-based knowledge; lessons learned from failures and successful activities; capturing tacit and undocumented knowledge and experience; the results of improvements in processes, products and services; learning from customers or external providers; standards; research papers; conferences; intellectual property.
注:组织知识的来源可包括:基于经验的知识;从失败和成功活动中吸取的教训;获取隐性和未形成文件的知识和经验;过程、产品和服务改进的结果;从顾客或外部提供方学习;标准;研究论文;会议;知识产权。
7.2 Competence
7.2 能力
The organization shall:
组织应:
a) determine the necessary competence of person(s) doing work under its control that affects its quality management system performance;
a) 确定在其控制下从事影响其质量管理体系绩效工作的人员所必需的能力;
b) ensure that these persons are competent on the basis of appropriate education, training, or experience;
b) 确保这些人员在适当的教育、培训或经验的基础上具备能力;
c) where applicable, take actions to acquire the necessary competence, and evaluate the effectiveness of the actions taken.
c) 适当时,采取措施以获得必要的能力,并评价所采取措施的有效性。
Appropriate documented information shall be available as evidence of competence.
应提供适当的形成文件的信息,作为能力的证据。
NOTE Applicable actions can include, for example, the provision of training to, the mentoring of, or the re-assignment of currently employed persons; or the hiring or contracting of competent persons.
注:适用的措施可包括,例如,对现有员工提供培训、指导或重新分配岗位;或招聘、外包有能力的人员。
7.3 Awareness
7.3 意识
The organization shall ensure that persons doing work under the organization's control are aware of:
组织应确保在其控制下工作的人员意识到:
a) the quality policy;
a) 质量方针;
b) their contribution to the effectiveness of the quality management system, including the benefits of improved performance;
b) 他们对质量管理体系有效性的贡献,包括绩效改进带来的好处;
c) the implications of not conforming with the quality management system requirements;
c) 不符合质量管理体系要求的后果;
d) relevant quality objectives;
d) 相关的质量目标;
e) organizational quality culture and ethical behaviour.
e) 组织的质量文化和道德行为。
7.4 Communication
7.4 沟通
The organization shall determine the internal and external communications relevant to the quality management system, including:
组织应确定与质量管理体系相关的内部和外部沟通,包括:
a) on what it will communicate;
a) 沟通什么内容;
b) when to communicate;
b) 何时沟通;
c) with whom to communicate;
c) 与谁沟通;
d) how to communicate;
d) 如何沟通;
e) who communicates.
e) 由谁沟通。
7.5 Documented information
7.5 形成文件的信息
7.5.1 General
7.5.1 总则
The organization's quality management system shall include:
组织的质量管理体系应包括:
a) documented information required by this document;
a) 本文件所要求的形成文件的信息;
b) documented information determined by the organization as being necessary for the effectiveness of the quality management system.
b) 组织确定的为确保质量管理体系有效性所需的形成文件的信息。
NOTE The extent of documented information for a quality management system can differ from one organization to another due to:
注:一个质量管理体系形成文件的信息的多少,可能因组织的以下不同而不同:
— the size of organization and its type of activities, processes, products and services;
— 组织的规模及其活动、过程、产品和服务的类型;
— the complexity of processes and their interactions;
— 过程及其相互作用的复杂程度;
— the competence of persons.
— 人员的能力。
7.5.2 Creating and updating documented information
7.5.2 创建和更新形成文件的信息
When creating and updating documented information, the organization shall ensure appropriate:
在创建和更新形成文件的信息时,组织应确保适当的:
a) identification and description (e.g. a title, date, author, or reference number);
a) 标识和说明(例如,标题、日期、作者或索引号);
b) format (e.g. language, software version, graphics) and media (e.g. paper, electronic);
b) 格式(例如,语言、软件版本、图表)和介质(例如,纸质、电子);
c) review and approval for suitability and adequacy.
c) 评审和批准,以确保其适宜性和充分性。
7.5.3 Control of documented information
7.5.3 形成文件的信息的控制
7.5.3.1 Documented information required by the quality management system and by this document shall be controlled to ensure:
7.5.3.1 质量管理体系和本文件所要求的形成文件的信息应予以控制,以确保:
a) it is available and suitable for use, where and when it is needed;
a) 在需要使用时,是可获得且适用的;
b) it is adequately protected (e.g. from loss of confidentiality, improper use, or loss of integrity).
b) 得到充分保护(例如,防止泄密、不当使用或失真)。
7.5.3.2 For the control of documented information, the organization shall address the following activities, as applicable:
7.5.3.2 为控制形成文件的信息,组织应针对以下活动采取措施(如适用):
a) distribution, access, retrieval and use;
a) 分发、访问、检索和使用;
b) storage and preservation, including preservation of legibility;
b) 存放和保护,包括保持清晰可辨;
c) control of changes (e.g. version control);
c) 变更的控制(例如,版本控制);
d) retention and disposition.
d) 保留和处置。
Documented information of external origin determined by the organization to be necessary for the planning and operation of the quality management system shall be identified as appropriate, and controlled.
组织确定的为策划和运行质量管理体系所必需的外来形成文件的信息,应得到适当识别和控制。
Documented information available as evidence of conformity shall be protected from unintended alterations.
作为符合性证据而提供的形成文件的信息应加以保护,防止非预期的篡改。
NOTE Access can imply a decision regarding the permission to view the documented information only, or the permission and authority to view and change the documented information.
注:访问可意味着决定仅允许查阅形成文件的信息,或决定允许并授权查阅和更改形成文件的信息。
8 Operation
8 运行
8.1 Operational planning and control
8.1 运行策划和控制
The organization shall plan, implement and control the processes needed to meet requirements for products and services, and to implement the actions determined in Clause 6, by:
组织应通过以下方式,策划、实施和控制满足产品和服务要求所需的过程,并实施第6章确定的措施:
a) establishing criteria for the processes;
a) 确定过程的准则;
b) implementing control of the processes in accordance with the criteria;
b) 按照准则实施对过程的控制;
c) establishing criteria for the acceptance of products and services;
c) 确定产品和服务的接收准则;
d) determining the resources needed to achieve conformity to the product and service requirements.
d) 确定为实现产品和服务要求符合性所需的资源。
Documented information shall be available to the extent necessary to have confidence that the processes have been carried out as planned.
应在必要范围内提供形成文件的信息,以确信过程已按策划实施。
The organization shall control planned changes and review the consequences of unintended changes, taking action to mitigate any adverse effects, as necessary.
组织应控制策划的变更,并评审非预期变更的后果,必要时采取措施减轻任何不利影响。
The organization shall ensure that externally provided processes, products or services that are relevant to the quality management-system are controlled (See 8.4).
组织应确保与质量管理体系相关的外部提供的过程、产品或服务得到控制(见8.4)。
Documented information shall be available to the extent necessary to demonstrate the conformity of products and services.
应在必要范围内提供形成文件的信息,以证实产品和服务的符合性。
8.2 Requirements for products and services
8.2 产品和服务的要求
8.2.1 Customer communication
8.2.1 顾客沟通
Communication with customers shall include:
与顾客的沟通应包括:
a) providing information relating to products and services;
a) 提供与产品和服务相关的信息;
b) handling enquiries, contracts or orders, including changes;
b) 处理问询、合同或订单,包括变更;
c) obtaining customer feedback relating to products and services, including customer complaints;
c) 获取与产品和服务相关的顾客反馈,包括顾客抱怨;
d) handling or controlling customer property;
d) 处理或控制顾客财产;
e) information related to contingency actions, including where relevant to any disruptions in the products or services provided.
e) 与应急措施相关的信息,包括与所提供的产品或服务中断相关的任何信息。
NOTE Customer communication can include direct contacts through meetings, electronic mails and document exchange or indirectly through web site content, publications, social media, responses to frequently asked questions, and training.
注:顾客沟通可包括通过会议、电子邮件和文件交换等直接联系,或通过网站内容、出版物、社交媒体、常见问题解答和培训等间接方式。
8.2.2 Determining the requirements for products and services
8.2.2 确定产品和服务的要求
When determining the requirements for the products and services to be offered to customers, the organization shall ensure that:
在确定要提供给顾客的产品和服务的要求时,组织应确保:
a) the requirements for the products and services are defined, including:
a) 产品和服务的要求得到确定,包括:
1) any applicable statutory and regulatory requirements;
1) 任何适用的法律法规要求;
2) those considered necessary by the organization;
2) 组织认为必要的要求;
b) the organization can meet the claims for the products and services it offers.
b) 组织能够满足其所提供的产品和服务的声明。
8.2.3 Review of the requirements for products and services
8.2.3 产品和服务的要求的评审
8.2.3.1 The organization shall ensure that it has the ability to meet the requirements for products and services to be offered to customers. The organization shall conduct a review before committing to supply products and services to a customer, to include:
8.2.3.1 组织应确保其有能力满足向顾客提供的产品和服务的要求。组织在承诺向顾客提供产品和服务之前应进行评审,评审应包括:
a) requirements specified by the customer, including the requirements for delivery and post-delivery activities when applicable;
a) 顾客规定的要求,适用时包括对交付及交付后活动的要求;
b) requirements not stated by the customer, but necessary for the specified or intended use, when known;
b) 顾客未规定,但已知是规定用途或已知预期用途所必需的要求;
c) requirements specified by the organization;
c) 组织规定的要求;
d) statutory and regulatory requirements applicable to the products and services;
d) 适用于产品和服务的法律法规要求;
e) contract or order requirements differing from those previously expressed.
e) 与以前表述不一致的合同或订单要求。
The organization shall ensure that contract or order requirements differing from those previously defined are resolved.
组织应确保与以前规定不一致的合同或订单要求得到解决。
The customer's requirements shall be confirmed by the organization before acceptance, when the customer does not provide a documented statement of their requirements.
当顾客未提供形成文件的要求说明时,组织在接受前应确认顾客的要求。
NOTE In some situations, such as internet sales, a formal review is impractical for each order. Instead, the review can cover relevant product information, such as websites or catalogues.
注:在某些情况下(如网上销售),对每个订单进行正式评审是不切实际的。此时,评审可涵盖相关的产品信息,如网站或产品目录。
8.2.3.2 Documented information shall be available as applicable, as evidence of:
8.2.3.2 应提供适用的形成文件的信息,作为以下证据:
a) the results of the review;
a) 评审的结果;
b) any new or changed requirements for the products and services.
b) 任何新的或变更的产品和服务要求。
8.2.4 Changes to requirements for products and services
8.2.4 产品和服务要求的变更
When requirements for products and services are changed, the organization shall ensure that relevant documented information is updated and communicated to relevant interested parties.
当产品和服务的要求发生变更时,组织应确保相关的形成文件的信息得到更新,并传达给相关方。
8.3 Design and development of products and services
8.3 产品和服务的设计和开发
8.3.1 General
8.3.1 总则
The organization shall establish, implement and maintain a design and development process that is appropriate to ensure the subsequent provision of products and services.
组织应建立、实施和保持一个适合于确保后续产品和服务提供的设计和开发过程。
NOTE The design and development process can include cycles of review, verification, validation and feedback, allowing for flexibility throughout the design and development phases.
注:设计和开发过程可包括评审、验证、确认和反馈的循环,从而在整个设计和开发阶段具有灵活性。
8.3.2 Design and development planning
8.3.2 设计和开发策划
In determining the stages and controls for design and development, the organization shall consider the:
在确定设计和开发的阶段和控制时,组织应考虑:
a) nature, duration and complexity of the design and development activities;
a) 设计和开发活动的性质、持续时间和复杂程度;
b) required process stages, including applicable design and development reviews;
b) 所要求的过程阶段,包括适用的设计和开发评审;
c) required design and development verification and validation activities;
c) 所要求的设计和开发验证与确认活动;
d) responsibilities and authorities involved in the design and development process;
d) 设计和开发过程所涉及的职责和权限;
e) internal and external resource needs for the design and development of products and services;
e) 产品和服务设计和开发所需的内部和外部资源;
f) need to control interfaces between persons involved in the design and development process;
f) 对参与设计和开发过程的人员之间接口进行控制的需求;
g) need for involvement of customers and users in the design and development process;
g) 在设计和开发过程中顾客和用户参与的需求;
h) requirements for subsequent provision of products and services;
h) 对后续产品和服务提供的要求;
i) level of control expected for the design and development process by customers and other relevant interested parties;
i) 顾客和其他相关方对设计和开发过程所期望的控制水平;
j) documented information needed as evidence that design and development requirements have been met.
j) 作为设计和开发要求已得到满足的证据所需的形成文件的信息。
8.3.3 Design and development inputs
8.3.3 设计和开发输入
The organization shall determine the requirements essential for the specific types of products and services to be designed and developed. The organization shall consider:
组织应确定待设计和开发的特定类型产品和服务所必需的要求。组织应考虑:
a) functional and performance requirements;
a) 功能和性能要求;
b) information derived from previous similar design and development activities;
b) 从以前类似的设计和开发活动中获得的信息;
c) statutory and regulatory requirements;
c) 法律法规要求;
d) standards or codes of practice that the organization has committed to implement;
d) 组织承诺实施的标准或实践准则;
e) potential consequences of failure due to the nature of the products and services.
e) 因产品和服务的性质而可能导致的失效后果。
Inputs shall be complete, unambiguous, and adequate for design and development purposes.
输入应是完整的、无歧义的,并能满足设计和开发的目的。
Conflicting design and development inputs shall be resolved.
相互矛盾的设计和开发输入应得到解决。
Documented information shall be available as evidence of design and development inputs.
应提供形成文件的信息,作为设计和开发输入的证据。
NOTE Design and development inputs are not always fully defined or known initially. Instead, they can evolve as the design progresses, through repeated cycles of development and validation.
注:设计和开发输入并非总是在初期就完全确定或已知。相反,它们可能随着设计的进展,通过重复的开发和验证循环而演变。
8.3.4 Design and development controls
8.3.4 设计和开发控制
The organization shall apply controls to the design and development process to ensure that:
组织应对设计和开发过程实施控制,以确保:
a) the results to be achieved are defined;
a) 要实现的结果得到确定;
b) reviews are conducted to evaluate the ability of the results of design and development to meet requirements;
b) 进行评审,以评价设计和开发的结果满足要求的能力;
c) verification activities are conducted to ensure that the design and development outputs meet the input requirements;
c) 进行验证活动,以确保设计和开发输出满足输入要求;
d) validation activities are conducted to ensure that the resulting products and services meet the requirements for the specified application or intended use;
d) 进行确认活动,以确保形成的产品和服务满足规定应用或预期用途的要求;
e) necessary actions are taken to address problems determined during the reviews, or verification and validation activities;
e) 采取必要措施,以解决在评审、验证和确认活动中发现的问题;
f) documented information is available as evidence of these activities.
f) 提供形成文件的信息,作为这些活动的证据。
NOTE Design and development reviews, verification and validation have distinct purposes. They can be conducted separately or in any combination, as is suitable for the products and services of the organization.
注:设计和开发的评审、验证和确认各有不同的目的。可以根据组织产品和服务的适宜性,单独或以任意组合的方式进行。
8.3.5 Design and development outputs
8.3.5 设计和开发输出
The organization shall ensure that design and development outputs:
组织应确保设计和开发输出:
a) meet the input requirements;
a) 满足输入要求;
b) are adequate for the subsequent processes for the provision of products and services;
b) 适用于产品和服务提供的后续过程;
c) include or reference monitoring and measuring requirements, as appropriate, and acceptance criteria;
c) 适当时,包括或引用监视和测量要求以及接收准则;
d) specify the characteristics of the products and services that are essential for their intended purpose and their safe and proper provision.
d) 规定对于其预期目的以及安全和正确提供至关重要的产品和服务特性。
Documented information shall be available as evidence of design and development outputs.
应提供形成文件的信息,作为设计和开发输出的证据。
8.3.6 Design and development changes
8.3.6 设计和开发变更
The organization shall determine, review and control changes made during, or subsequent to, the design and development of products and services, to the extent necessary to ensure that there is no adverse impact on conformity to requirements.
组织应确定、评审和控制在产品和服务的设计和开发期间或之后所做的变更,其程度应足以确保对要求的符合性没有不利影响。
Documented information shall be available as evidence of:
应提供形成文件的信息,作为以下证据:
a) design and development changes;
a) 设计和开发的变更;
b) the results of reviews;
b) 评审的结果;
c) the authorization of the changes;
c) 变更的授权;
d) the actions taken to prevent adverse impacts.
d) 为防止不利影响而采取的措施。
8.4 Control of externally provided processes, products and services
8.4 外部提供的过程、产品和服务的控制
8.4.1 General
8.4.1 总则
The organization shall ensure that externally provided processes, products and services conform to requirements.
组织应确保外部提供的过程、产品和服务符合要求。
The organization shall determine the controls to be applied to externally provided processes, products and services when:
组织应在以下情况时,确定对外部提供的过程、产品和服务实施的控制:
a) products and services from external providers are intended for incorporation into the organization's own products and services;
a) 来自外部提供方的产品和服务旨在并入组织自身的产品和服务中;
b) products and services are provided directly to customers by external providers on behalf of the organization;
b) 外部提供方代表组织直接向顾客提供产品和服务;
c) a process, or part of a process, is provided by an external provider as a result of a decision by the organization.
c) 经组织决定,由外部提供方提供某个过程或过程的一部分。
The organization shall determine and apply criteria for the evaluation, selection, monitoring of performance, and re-evaluation of external providers, based on their ability to provide processes, products or services in accordance with requirements. Documented information shall be available as evidence of these activities and any necessary actions arising from the evaluations.
组织应基于外部提供方根据要求提供过程、产品或服务的能力,确定并应用对其评价、选择、绩效监视和重新评价的准则。应提供形成文件的信息,作为这些活动以及由评价而产生的任何必要措施的证据。
8.4.2 Type and extent of control
8.4.2 控制的类型和程度
The organization shall ensure that externally provided processes, products and services do not adversely affect the organization's ability to consistently deliver conforming products and services to its customers.
组织应确保外部提供的过程、产品和服务不会对组织持续向其顾客交付合格产品和服务的能力产生不利影响。
The organization shall:
组织应:
a) ensure that externally provided processes remain within the control of its quality management system;
a) 确保外部提供的过程保持在其质量管理体系的控制之内;
b) define both the controls that it intends to apply to an external provider and those it intends to apply to the resulting output;
b) 确定其计划对外部提供方实施的控制,以及计划对结果输出实施的控制;
c) take into consideration:
c) 考虑:
1) the potential impact of the externally provided processes, products and services on the organization's ability to consistently meet customer and applicable statutory and regulatory requirements;
1) 外部提供的过程、产品和服务对组织持续满足顾客要求及适用法律法规要求能力的潜在影响;
2) the effectiveness of the controls applied by the external provider;
2) 外部提供方所实施控制的有效性;
d) determine the verification, or other activities, necessary to ensure that the externally provided processes, products and services meet requirements.
d) 确定为确保外部提供的过程、产品和服务满足要求所必需的验证或其他活动。
8.4.3 Information for external providers
8.4.3 给外部提供方的信息
The organization shall ensure the adequacy of requirements prior to their communication to the external provider.
组织在与外部提供方沟通之前,应确保要求的充分性。
The organization shall communicate to external providers its requirements, as appropriate, for:
组织应酌情向外部提供方沟通其在以下方面的要求:
a) the processes, products and services to be provided;
a) 拟提供的过程、产品和服务;
b) the approval of:
b) 对以下各项的批准:
1) products and services;
1) 产品和服务;
2) methods, processes and equipment;
2) 方法、过程和设备;
3) the release of products and services;
3) 产品和服务的放行;
c) competence, including any required qualification of persons;
c) 能力,包括对人员的任何资格要求;
d) the external providers' interactions with the organization and, where applicable, it's customers and other relevant interested parties;
d) 外部提供方与组织的互动,适用时,还包括与其顾客和其他相关方的互动;
e) control and monitoring of the external providers' performance to be applied by the organization;
e) 组织对外部提供方绩效的控制和监视;
f) verification or validation activities that the organization, or its customer, intends to perform at the external providers' premises.
f) 组织或其顾客拟在外部提供方现场进行的验证或确认活动。
8.5 Production and service provision
8.5 生产和服务提供
8.5.1 Control of production and service provision
8.5.1 生产和服务提供的控制
The organization shall implement production and service provision under controlled conditions.
组织应在受控条件下实施生产和服务提供。
Controlled conditions shall include, as applicable:
受控条件应包括(如适用):
a) the availability and use of documented information that defines:
a) 可获得并使用确定了以下内容的形成文件的信息:
1) the characteristics of the products to be produced or the services to be provided;
1) 拟生产的产品或拟提供的服务的特性;
2) the activities to be performed;
2) 拟实施的活动;
3) the results to be achieved;
3) 拟实现的结果;
b) the availability and use of suitable monitoring and measuring resources;
b) 可获得并使用适宜的监视和测量资源;
c) the implementation of monitoring and measurement activities at appropriate stages to verify that criteria for control of processes or outputs, and acceptance criteria for products and services, have been met;
c) 在适当阶段实施监视和测量活动,以验证过程或输出的控制准则以及产品和服务的接收准-则已得到满足;
d) the use of suitable infrastructure and environment for the operation of processes;
d) 为过程运行使用适宜的基础设施和环境;
e) the appointment of competent persons, including any required qualification;
e) 任用有能力的人员,包括任何要求的资格;
f) the validation, and periodic revalidation, of the ability to achieve planned results of the processes for production and service provision, where the resulting output cannot be verified by subsequent monitoring or measurement;
f) 当生产和服务提供过程的结果输出无法由后续的监视或测量加以验证时,对该过程实现所策划结果的能力进行确认,及定期的再确认;
g) the implementation of actions to prevent human error;
g) 实施预防人为错误的措施;
h) the implementation of release, delivery and post-delivery activities.
h) 实施放行、交付和交付后活动。
NOTE To ensure that the defined requirements are met, organizations can choose to engage in product and service verification or process validation activities, or both, as appropriate.
注:为确保满足规定的要求,组织可酌情选择进行产品和服务验证或过程确认活动,或两者兼而有之。
8.5.2 Identification and traceability
8.5.2 标识和可追溯性
The organization shall:
组织应:
a) use suitable means to identify outputs when it is necessary to ensure the conformity of products and services;
a) 在为确保产品和服务的符合性所必要时,使用适宜的方法识别输出;
b) identify the status of outputs with respect to monitoring and measurement requirements throughout production and service provision;
b) 在整个生产和服务提供过程中,识别输出相对于监视和测量要求的状态;
c) control the unique identification of the outputs when traceability is a requirement, and shall ensure that documented information necessary to enable traceability is available as evidence.
c) 当可追溯性是要求时,控制输出的唯一性标识,并应确保为实现可追溯性所必需的形成文件的信息可作为证据。
8.5.3 Property belonging to customers or external providers
8.5.3 顾客或外部提供方的财产
The organization shall exercise care with property belonging to customers or external providers while it is under the organization's control or being used by the organization.
组织应对其控制下或其使用的顾客或外部提供方的财产予以爱护。
The organization shall identify, verify, protect and safeguard customers' or external providers' property provided for use or incorporation into the products and services.
组织应对被提供用于产品和服务或构成产品和服务一部分的顾客或外部提供方的财产进行识别、验证、保护和防护。
When the property of a customer or external provider is lost, damaged or otherwise found to be unsuitable for use, the organization shall report this to the customer or external provider and ensure that documented information is available as evidence of what has occurred.
当顾客或外部提供方的财产发生丢失、损坏或发现不适用时,组织应向顾客或外部提供方报告,并确保提供形成文件的信息作为所发生事件的证据。
NOTE A customer's or external provider's property can include materials, components, tools and equipment, premises, intellectual property and personal data.
注:顾客或外部提供方的财产可包括材料、部件、工具和设备、场所、知识产权和个人数据。
8.5.4 Preservation
8.5.4 防护
The organization shall preserve the outputs during production and service provision, to the extent necessary to ensure conformity to requirements.
组织应在生产和服务提供期间对输出进行防护,其程度应足以确保对要求的符合性。
NOTE Preservation can include identification, handling, contamination control, packaging, storage, transmission or transportation, and protection.
注:防护可包括标识、处置、污染控制、包装、储存、传输或运输及保护。
8.5.5 Post-delivery activities
8.5.5 交付后活动
The organization shall meet requirements for post-delivery activities associated with the products and services.
组织应满足与产品和服务相关的交付后活动的要求。
In determining the extent of post-delivery activities that are required, the organization shall consider:
在确定所需的交付后活动的范围时,组织应考虑:
a) statutory and regulatory requirements;
a) 法律法规要求;
b) the potential undesired consequences associated with its products and services;
b) 与其产品和服务相关的潜在不期望的后果;
c) the nature, use and intended lifetime of its products and services;
c) 其产品和服务的性质、用途和预期寿命;
d) customer requirements;
d) 顾客要求;
e) customer feedback.
e) 顾客反馈。
NOTE Post-delivery activities can include actions under warranty provisions, contractual obligations such as maintenance services, and supplementary services such as recycling or final disposal.
注:交付后活动可包括保修条款下的措施、合同义务(如维护服务),以及辅助服务(如回收或最终处置)。
8.5.6 Control of changes
8.5.6 变更控制
The organization shall review and control changes for production or service provision, to the extent necessary to ensure continuing conformity with requirements.
组织应对生产或服务提供的变更进行评审和控制,其程度应足以确保持续符合要求。
Documented information shall be available as evidence of the results of the review of changes, the person or persons authorizing the change, and any necessary actions arising from the review.
应提供形成文件的信息,作为变更评审结果、授权变更的人员以及因评审而采取的任何必要措施的证据。
8.6 Release of products and services
8.6 产品和服务的放行
The organization shall implement planned arrangements, at appropriate stages, to verify that the product and service requirements have been met.
组织应在适当阶段实施所策划的安排,以验证产品和服务的要求已得到满足。
The release of products and services to the customer shall not proceed until the planned arrangements have been satisfactorily completed, unless otherwise approved by a relevant authority and, as applicable, by the customer.
除非得到相关授权人员的批准,适用时得到顾客的批准,否则在所策划的安排已圆满完成之前,不得向顾客放行产品和服务。
Documented information shall be available as evidence on the release of products and services. The documented information shall include:
应提供形成文件的信息,作为产品和服务放行的证据。该形成文件的信息应包括:
a) evidence of conformity with the acceptance criteria;
a) 符合接收准则的证据;
b) traceability to the person or persons authorizing the release.
b) 可追溯到授权放行的人员。
8.7 Control of nonconforming outputs
8.7 不合格输出的控制
8.7.1 The organization shall ensure that outputs that do not conform to requirements are identified and controlled to prevent their unintended use or delivery.
8.7.1 组织应确保对不符合要求的输出进行识别和控制,以防止其非预期的使用或交付。
The organization shall take appropriate action based on the nature of the nonconformity and its effect on the conformity of products and services. This shall also apply to nonconforming products and services detected after delivery of products, during or after the provision of services.
组织应根据不符合的性质及其对产品和服务符合性的影响,采取适当的措施。这也应适用于在产品交付之后、服务提供期间或之后发现的不合格产品和服务。
The organization shall deal with nonconforming outputs in one or more of the following ways:
组织应通过以下一种或多种方式处置不合格输出:
a) correction;
a) 纠正;
b) segregation, containment, return or suspension of provision of products and services;
b) 隔离、封存、退货或暂停提供产品和服务;
c) informing the customer;
c) 通知顾客;
d) obtaining authorization for acceptance under concession.
d) 获得让步接收的授权。
Conformity to the requirements shall be verified when nonconforming outputs are corrected.
当不合格输出得到纠正后,应对其是否符合要求进行验证。
8.7.2 Documented information shall be available as evidence to:
8.7.2 应提供形成文件的信息,作为以下证据:
a) describe the nonconformity;
a) 描述不符合;
b) describe the actions taken;
b) 描述所采取的措施;
c) describe any concessions obtained;
c) 描述所获得的任何让步;
d) identify the authority deciding the action in respect of the nonconformity.
d) 识别决定对不符合采取措施的授权人员。
9 Performance evaluation
9 绩效评价
9.1 Monitoring, measurement, analysis and evaluation
9.1 监视、测量、分析和评价
9.1.1 General
9.1.1 总则
The organization shall determine:
组织应确定:
a) what needs to be monitored and measured;
a) 需要监视和测量的对象;
b) the methods for monitoring, measurement, analysis and evaluation, as applicable, needed to ensure valid results;
b) 为确保结果有效所需的监视、测量、分析和评价方法(如适用);
c) when the monitoring and measuring shall be performed;
c) 实施监视和测量的时间;
d) when the results from monitoring and measurement shall be analysed and evaluated.
d) 分析和评价监视和测量结果的时间。
The organization shall evaluate the performance and the effectiveness of the quality management system.
组织应评价质量管理体系的绩效和有效性。
Documented information shall be available as evidence of the results.
应提供形成文件的信息,作为结果的证据。
9.1.2 Customer satisfaction
9.1.2 顾客满意
The organization shall monitor the customers' satisfaction. The organization shall determine the methods for obtaining, monitoring and reviewing this information.
组织应监视顾客的满意程度。组织应确定获取、监视和评审这些信息的方法。
NOTE Sources of information to support understanding of customer satisfaction can include customer surveys, customer feedback on delivered products and services, meetings with customers, market-share analysis, compliments, warranty claims and dealer reports, complaints and social media.
注:有助于理解顾客满意度的信息来源可包括顾客调查、对已交付产品和服务的顾客反馈、与顾客的会议、市场份额分析、赞扬、保修索赔和经销商报告、投诉以及社交媒体。
9.1.3 Analysis and evaluation
9.1.3 分析和评价
The organization shall analyse and evaluate relevant data and information arising from monitoring and measurement.
组织应分析和评价从监视和测量中获得的适宜的数据和信息。
The results of analysis shall be used to evaluate:
分析结果应用于评价:
a) conformity of products and services;
a) 产品和服务的符合性;
b) the degree of customer satisfaction;
b) 顾客满意程度;
c) the performance and effectiveness of the quality management system;
c) 质量管理体系的绩效和有效性;
d) if planning has been implemented effectively;
d) 策划是否已得到有效实施;
e) the effectiveness of actions taken to address risks and opportunities;
e) 应对风险和机遇所采取措施的有效性;
f) the performance of external providers;
f) 外部提供方的绩效;
g) the need for improvements to the quality management system.
g) 对质量管理体系进行改进的需求。
NOTE Methods to analyse data can include statistical techniques.
注:数据分析方法可包括统计技术。
9.2 Internal audit
9.2 内部审核
9.2.1 General
9.2.1 总则
The organization shall conduct internal audits at planned intervals to provide information on whether the quality management system:
组织应按策划的时间间隔进行内部审核,以提供关于质量管理体系是否满足以下两方面要求的信息:
a) conforms to:
a) 符合:
1) the organization's own requirements for its quality management system;
1) 组织自身为其质量管理体系规定的要求;
2) the requirements of this document;
2) 本文件的要求;
b) is effectively implemented and maintained.
b) 得到有效实施和保持。
9.2.2 Internal audit programme
9.2.2 内部审核方案
The organization shall plan, establish, implement and maintain (an) audit programme(s) including the frequency, methods, responsibilities, planning requirements and reporting.
组织应策划、建立、实施和保持一个或多个审核方案,包括审核的频次、方法、职责、策划要求和报告。
When establishing the internal audit programme(s), the organization shall consider the importance of the processes concerned and the results of previous audits, and changes affecting the organization.
在建立内部审核方案时,组织应考虑相关过程的重要性、以往审核的结果以及影响组织的变化。
The organization shall:
组织应:
a) define the audit objectives, criteria and scope for each audit;
a) 为每次审核确定审核目标、准则和范围;
b) select auditors and conduct audits to ensure objectivity and the impartiality of the audit process;
b) 遴选审核员并实施审核,以确保审核过程的客观和公正;
c) ensure that the results of audits are reported to relevant managers;
c) 确保将审核结果报告给相关管理者;
d) take appropriate correction and corrective actions without undue delay.
d) 及时采取适当的纠正和纠正措施。
Documented information shall be available as evidence of the implementation of the audit programme(s) and the audit results.
应提供形成文件的信息,作为审核方案实施和审核结果的证据。
NOTE See ISO 19011[4] for guidance on auditing management systems.
注:关于管理体系审核的指南,见ISO 19011[4]。
9.3 Management review
9.3 管理评审
9.3.1 General
9.3.1 总则
Top management shall review the organization's quality management system, at planned intervals, to ensure its continuing suitability, adequacy, effectiveness, and alignment with the strategic direction of the organization.
最高管理者应按策划的时间间隔评审组织的质量管理体系,以确保其持续的适宜性、充分性、有效性,并与组织的战略方向保持一致。
9.3.2 Management review inputs
9.3.2 管理评审输入
The management review shall include:
管理评审应包括:
a) the status of actions from previous management reviews;
a) 以往管理评审所采取措施的状况;
b) changes in external and internal issues that are relevant to the quality management system;
b) 与质量管理体系相关的外部和内部问题的变化;
c) changes in needs and expectations of interested parties that are relevant to the quality management system;
c) 与质量管理体系相关的相关方的需求和期望的变化;
d) information on the quality management system performance including trends in:
d) 质量管理体系的绩效信息,包括以下方面的趋势:
1) nonconformities and corrective actions;
1) 不符合和纠正措施;
2) monitoring and measurement results;
2) 监视和测量结果;
3) audit results;
3) 审核结果;
4) customer satisfaction and feedback from relevant interested parties;
4) 顾客满意和来自相关方的反馈;
5) the extent to which quality objectives have been met;
5) 质量目标的实现程度;
6) process performance and conformity of products and services;
6) 过程绩效以及产品和服务的符合性;
7) the performance of external providers;
7) 外部提供方的绩效;
e) opportunities for improvement;
e) 改进的机会;
f) the adequacy of resources;
f) 资源的充分性;
g) the effectiveness of actions taken to address risks and opportunities (see 6.1).
g) 为应对风险和机遇所采取措施的有效性(见6.1)。
9.3.3 Management review results
9.3.3 管理评审结果
The results of the management review shall include decisions related to continual improvement opportunities and any need for changes to the quality management system or resource needs.
管理评审的结果应包括与持续改进机会相关的决策,以及对质量管理体系或资源需求的任何变更需求。
Documented information shall be available as evidence of the results of management reviews.
应提供形成文件的信息,作为管理评审结果的证据。
10 Improvement
10 改进
10.1 Continual improvement
10.1 持续改进
The organization shall continually improve the suitability, adequacy and effectiveness of the quality management system.
组织应持续改进质量管理体系的适宜性、充分性和有效性。
The organization shall consider the results of monitoring, measurement, analysis and evaluation of data and information, and the results of management review, to determine opportunities that shall be addressed as part of continual improvement.
组织应考虑数据和信息的监视、测量、分析和评价结果,以及管理评审的结果,以确定应作为持续改进一部分来处理的机会。
Actions shall include:
措施应包括:
a) improving processes, products and services;
a) 改进过程、产品和服务;
b) addressing future needs and expectations;
b) 应对未来的需求和期望;
c) correcting, preventing or reducing undesired effects.
c) 纠正、预防或减少不良影响。
NOTE Improvement can be achieved through incremental and breakthrough change, innovation or re-organization initiatives.
注:改进可以通过渐进式和突破性变革、创新或重组等举措来实现。
10.2 Nonconformity and corrective action
10.2 不符合和纠正措施
10.2.1 When a nonconformity occurs, the organization shall:
10.2.1 当发生不符合时,组织应:
a) react to the nonconformity and, as applicable:
a) 对不符合做出反应,并适当时:
1) take action to control and correct it;
1) 采取措施对其进行控制和纠正;
2) deal with the consequences;
2) 处理其后果;
b) evaluate the need for action to eliminate the cause(s) of the nonconformity, in order that it does not recur or occur elsewhere, by:
b) 通过以下方式,评价为消除不符合原因以防止其再次发生或在别处发生而采取措施的需求:
1) reviewing the nonconformity;
1) 评审不符合;
2) determining the causes of the nonconformity;
2) 确定不符合的原因;
3) determining if similar nonconformities exist, or can potentially occur;
3) 确定是否存在或可能发生类似的不符合;
c) implement any action needed;
c) 实施任何必要的措施;
d) review the effectiveness of any corrective action taken;
d) 评审所采取的任何纠正措施的有效性;
e) update risks and opportunities determined during planning, if necessary;
e) 如有必要,更新在策划期间确定的风险和机遇;
f) make changes to the quality management system, if necessary.
f) 如有必要,对质量管理体系进行变更。
Corrective actions shall be appropriate to the effects of the nonconformities encountered.
纠正措施应与所遇到不符合的影响相适应。
NOTE Customer complaints can be a source of nonconformities.
注:顾客抱怨可能是不符合的一个来源。
10.2.2 Documented information shall be available as evidence of:
10.2.2 应提供形成文件的信息,作为以下证据:
a) the nature of the nonconformities and any subsequent actions taken;
a) 不符合的性质以及随后采取的任何措施;
b) the results of any corrective action.
b) 任何纠正措施的结果。
2026-02-09
2026-02-08
2026-02-06
2026-02-05
2026-02-04
2026-02-04



